Standalone Angular folder structure
Starting with Angular 17 release, creating an Angular application with ng new will generate a Standalone application by default.
Not only it’ll introduce some changes in the way you organize your application but that’s a good opportunity to review the architecture itself by now!
This article focuses on the content of your src/app folder, and how to organize it to make it easier to maintain and scale.
For convenience, the structure examples won’t include the default files created at the root of the src/app folder by the Angular CLI:
src└── app ├── app.component.ts ├── app.component.spec.ts ├── app.component.html ├── app.component.css ├── app.routes.ts ├── app.config.tsTypes of content
There are three types of code content in the src/app folder:
- the code specific to a non business feature
- the code specific to a business feature
- the code shared between features

That’s commonly translated into the following folder structure:
src└── app ├── core ├── features └── shared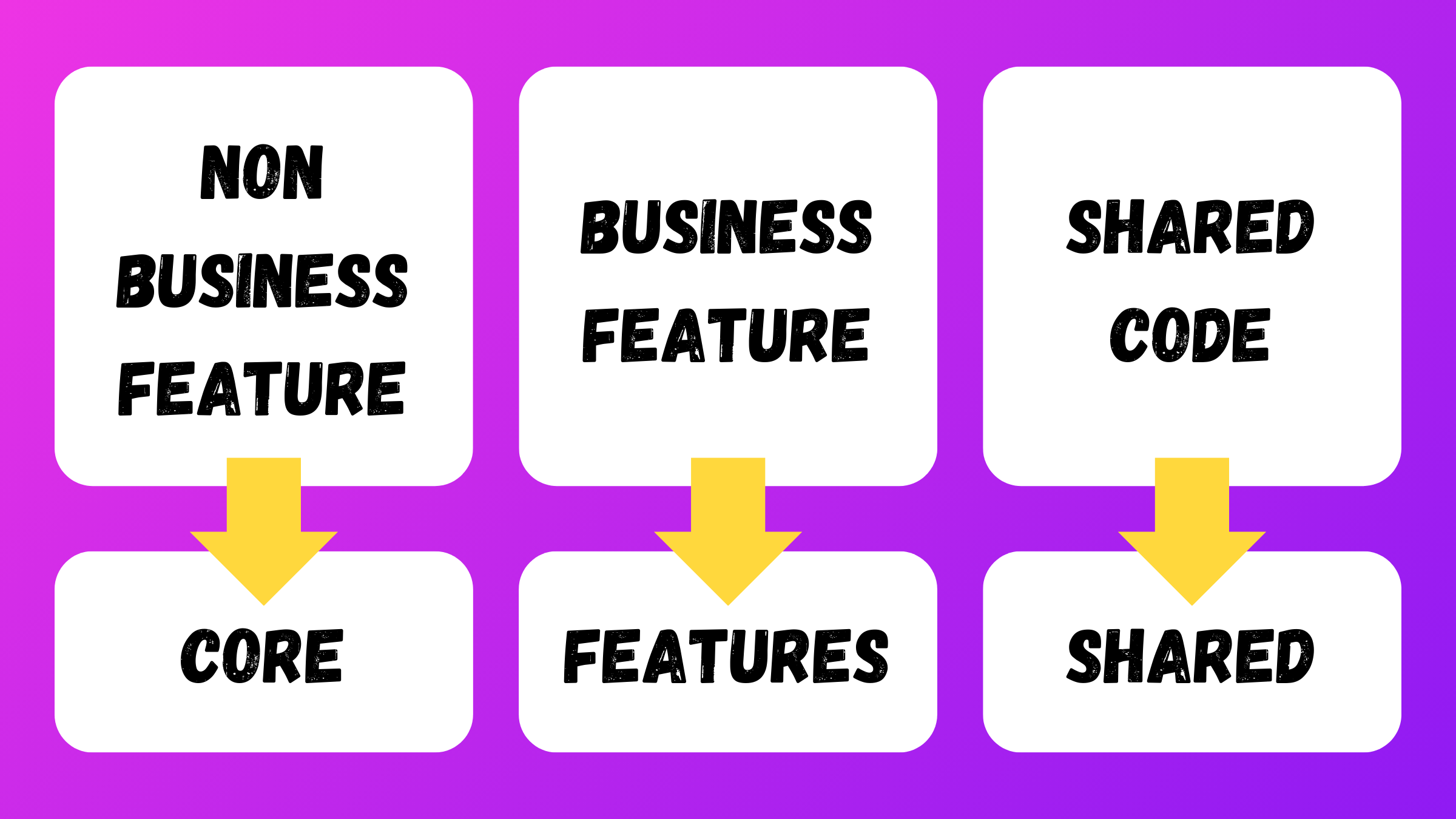
That’s the first level of organization of your application, with a dedicated folder for each type of content.
Non business feature (core folder)

A non business feature is a feature that is not specific to the business domain of the application.
Some examples are:
- the layout of your application
- the authentication process.
For this content, you’ll want to create a dedicated folder in the src/app/core folder.
src└── app └── core ├── layout └── authLet’s take a closer look at the auth folder as an example!
Authentication
Common features of an authentication process are:
- the login page
- the registration page
- the password recovery page
You will also want to define:
- the user model
- the authentication service to communicate with the server
- the authentication guard to protect routes
Let’s organize these files!
Pages
We want to differenciate the routed components from the rest of the code. To do so, create a dedicated folder for the pages of the feature and a routing file to define the routes of the feature.
At this point your core folder will look like this:
src└── app └── core └── auth ├── auth.routes.ts └── pages ├── login ├── register ├── password-recoveryIf your feature only includes 1 route, you can declare it in your
src/app/app.routes.tsfile. In this situation, do not create a dedicatedauth.routes.tsfile.
Global authentication code
While being specific to the authentication feature, some code is shared between the different pages of the feature, or even more.
The user model, the authentication service are shared between the different pages of the auth feature.
The authentication guard is shared between the different pages of the whole application.
Create a dedicated folder for each type of content:
src└── app └── core └── auth ├── auth.service.ts ├── auth.service.spec.ts ├── auth.model.ts ├── auth.guard.ts ├── auth.guard.spec.ts ├── auth.routes.ts └── pages ├── login ├── register ├── password-recoveryIf you know that you’ll have more than one related file in the future, create dedicated folders for each type of content from the beginning:
src└── app └── core └── auth ├── models └── auth.model.ts ├── guards └── auth.guard.ts └── auth.guard.spec.ts ├── services └── auth.service.spec.ts ├── auth.routes.ts └── pages ├── login ├── register ├── password-recoveryPages folders
The pages folders are used to store the routed component and all the related and specific code of a page. At the root of the folder, you’ll find the routed component, and more folders for content shared between the different pages of the feature:
componentsfor the components used in the pagesservicesfor the services used in the pagesmodelsfor the models used in the pagesdirectivesfor the directives used in the pagespipesfor the pipes used in the pages
The folder will look like this:
src└── app └── core └── auth └── pages ├── login ├── login.component.ts ├── login.component.spec.ts ├── login.component.html ├── login.component.css ├── components ├── services ├── models ├── directives ├── pipes ├── register ├── password-recoveryApply the same logic to the other features of your core folder.
Isolated non business feature
Some features might be as simple as a service or a directive.
To simplify your structure, you might not want to create a dedicated folder for them in the src/app/core folder.
In this situation, place the code directly at the root of the folder, in a folder based on its technical shape (services, directives, pipes, …).
Like these notification.service.ts and api.service.ts files:
src└── app └── core ├── services └── notification.service.ts └── notification.servicespec.ts ├── interceptors └── api.interceptor.ts └── api.interceptor.spec.ts ├── auth ├── auth.service.ts ├── auth.service.spec.ts ├── auth.model.ts ├── auth.guard.ts ├── auth.guard.spec.ts ├── auth.routes.ts └── pages ├── login ├── register ├── password-recoveryBusiness feature

A business feature is a feature that is specific to the business domain of the application. Some examples are for e-commerce applications: the product list, the loyalty program, the cart, and the checkout process.
This code lives in the src/app/features folder.
This folder uses the same logic as the core folder:
- a dedicated folder for each feature
- a dedicated folder for the pages of the feature
- more folders for content shared between the different pages of the feature
There is one exception though!
While you can have some isolated pieces of code at the root of the src/app/core folder, you won’t have any at the root of the src/app/features folder.
It’s all about business isolated features.
src└── app └── features ├── product ├── cart ├── checkout ├── checkout.service.ts ├── checkout.service.spec.ts ├── checkout.model.ts ├── checkout.guard.ts ├── checkout.guard.spec.ts ├── checkout.routes.ts └── pages ├── address ├── paymentShared code

The shared code is the code that is shared between the different features of the application. There are two kind of code being shared between features:
- the one including some business logic
- the one that doesn’t.
The shared code lives in the src/app/shared folder.
Dumbed shared code
You might have heard about dumb components and smart components. The dumb components are the components that don’t include any business logic.
Let’s take a notification component as an example.
Even if the data to fill it comes from a business feature, the notification should not care.
If it expects a title and a message, it should not care about the origin of the title and the message.
And its @Input should be named title and message, not productTitle and productMessage.
Such a component is perfectly suited to be placed in the src/app/shared folder.
Such components, pipes and some util functions are the perfect example of ‘dumb’ shared code.
src└── app └── shared ├── components ├── notification.component.ts ├── notification.component.spec.ts ├── notification.component.html ├── notification.component.css ├── pipes ├── date.pipe.ts ├── date.pipe.spec.ts ├── utils ├── array.utils.ts ├── array.utils.spec.tsSmart shared code
The ‘smart’ shared code is the code that includes some business logic. Where to put it as it’s both shared and business specific?
There are two strategies to handle this situation:
- place this content in the
src/app/sharedfolder - place this content in the related feature folder in the
src/app/featuresfolder
I encourage to use the second solution, as it makes the code more discoverable and easier to maintain. That’s quite common for a feature to include some part of another one.
It can be about Shared UI content, like a product-card component, or shared business logic, like a product.service or a product.model.
Placing it in the shared folder will quickly lead to have too much content there, making it hard to maintain.
Here is a resume of the whole application structure:
src└── app ├── core ├── layout ├── auth ├── auth.service.ts ├── auth.service.spec.ts ├── auth.model.ts ├── auth.guard.ts ├── auth.guard.spec.ts ├── auth.routes.ts └── pages ├── login ├── register ├── password-recovery ├── services └── notification.service.ts └── notification.service.spec.ts ├── interceptors └── api.interceptor.ts └── api.interceptor.spec.ts └── features ├── product ├── cart ├── checkout ├── checkout.service.ts ├── checkout.service.spec.ts ├── checkout.model.ts ├── checkout.guard.ts ├── checkout.guard.spec.ts ├── checkout.routes.ts └── pages ├── address ├── payment └── shared ├── components ├── notification.component.ts ├── notification.component.spec.ts ├── notification.component.html ├── notification.component.css ├── pipes ├── date.pipe.ts ├── date.pipe.spec.ts ├── utils ├── array.utils.ts ├── array.utils.spec.tsAngular RealWorld Example App is a good example of a real-world application using this structure.
